Is Maltodextrin Dairy Free
Yes, it’s definitely dairy-free (Dairy-Free). Pure maltodextrin is a safe ingredient for individuals with lactose intolerance or a milk allergy. At its root, maltodextrin is not derived from milk or any dairy product, but is purely a plant extract. It is the carbohydrate derived from the starch of corn, rice, potatoes and even wheat. In the food industry, its role is usually a thickener, preservative or texture enhancer to improve taste, and it is widely found in a variety of packaged foods from salad dressings to protein powders. So, the next time you see the word “maltodextrin” on a food label, you don’t need to worry about any “invisible” milk protein or lactose hidden in it.
The Plant-Based Origins Of Maltodextrin
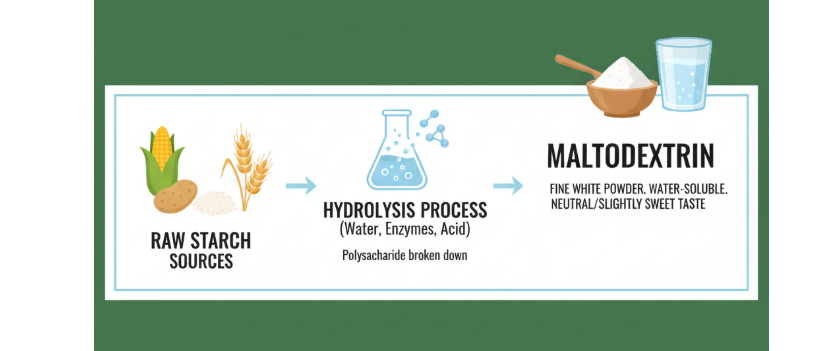
To understand why maltodextrin is suitable for a dairy-free diet, we have to look at its “origin”. It is essentially a polysaccharide (Polysaccharide), that is, it is a carbohydrate made of multiple sugar molecules bonded together. The manufacturer produces this fine white powder through a process called “hydrolysis” (hydrolysis). Simply put, starch from corn, potatoes, rice or wheat is broken down using water, enzymes and acid. This process ultimately produces a water-soluble powder with a neutral or slightly sweet taste.
It is worth mentioning that the source of raw materials in different regions will be different. In the United States, maltodextrin is overwhelmingly made from corn; in Europe, wheat is the more common source of raw materials. Although this does not affect its “dairy free” properties, it is worth paying attention to when dealing with gluten issues.
Why It’s Safe For Lactose Intolerance And Milk Allergies
In clinical practice, understanding the difference between “lactose intolerance” and “milk allergy” is the key to understanding the safety of maltodextrin. Many people tend to confuse the two, but their mechanisms are completely different.
Lactose intolerance (Lactose Intolerance): This is primarily a digestive problem. The patient’s body cannot easily break down lactose (the main sugar in milk). Since maltodextrin is a derivative of plant starch, it is naturally lactose-free. In fact, I often see maltodextrin used as a carbohydrate substitute for lactose in some special lactose-free formulas or foods.
Milk allergy (Milk Allergy): This is a reaction of the immune system, the body will reject the protein in milk (such as casein and whey protein). Maltodextrin is a carbohydrate, not a protein, and it is derived from plants. This means that it does not contain any milk protein at all. So, from the perspective of component analysis, it is safe for milk allergy patients.
To the forefront of nutrition
Always provide high standards of food additives and nutrition.Delivering innovative solutions that enhance the flavor, texture, and nutritional profile of food,supporting healthier, sustainable products for the food industry.
Common Uses Of Maltodextrin
As the food additive, maltodextrin is so popular because it is too “easy to use”—it can improve the texture, enhance the flavor, extend the shelf life, and it does not have a strong taste, so it will not steal the limelight of the main ingredient. You may be consuming it every day without realizing it. Here are a few types of food that I often see in the ingredient list:
- Sauce and salad dressing: here it mainly acts as a thickener, giving a richer and smoother taste.
- Packaged snacks: such as potato chips and biscuits, it can improve the taste, while being used as a filler (filler).
- Sweeteners and desserts: In artificial sweeteners and baked goods, it is often used as a bulking agent to add bulk.
- Sports and energy drinks: For fitness people, it is the carbohydrate that can be digested quickly and can provide instant energy supplement.
- Instant Soups and Seasonings: It helps to stabilize the ingredients and make the instant soup powder or spice packets thicker after brewing.

Author:Colton
As a food-conscious individual who once spent hours deciphering ingredient lists, I understand the challenge of navigating a dairy-free diet. After researching ingredients like maltodextrin, I’m here to share what I’ve learned, helping you shop with confidence and enjoy your food without worry.
 SGNUTRI
SGNUTRI